Managing hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) starts with understanding the condition1,2
HS can be a debilitating, under-recognized condition that can affect many aspects of a patient's life.3-5 But with proper education, management strategies, and resources, you may be able to help prevent irreversible skin damage.1,2 Awareness can support better outcomes for patients, and you can support increased awareness for your peers.4,6 Help shine a light on HS.
What is hidradenitis suppurativa?
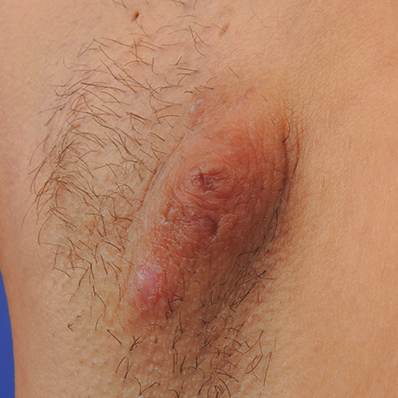
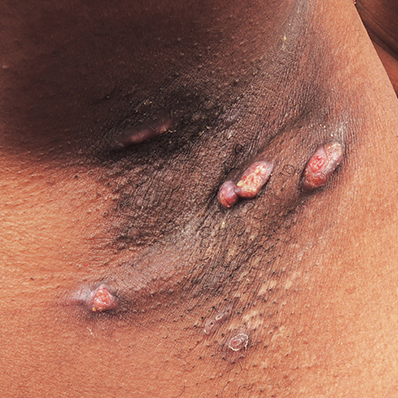
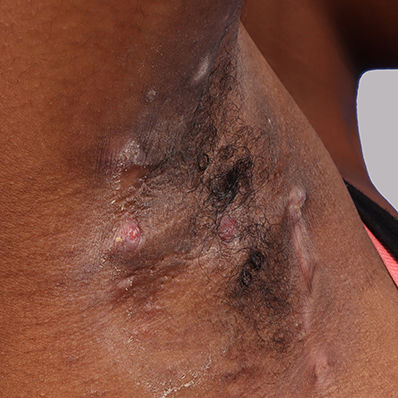
Hidradenitis suppurativa, commonly referred to as HS and also known as acne inversa, is a chronic, often progressive, systemic, inflammatory skin condition that commonly manifests as subcutaneous nodules and abscesses in flexural sites, such as the groin or axillae.3,7 If left untreated, HS may advance quickly.8,9 Timely intervention is needed to help prevent permanent damage.3
Images provided by Science Source
Early recognition and intervention are critical3
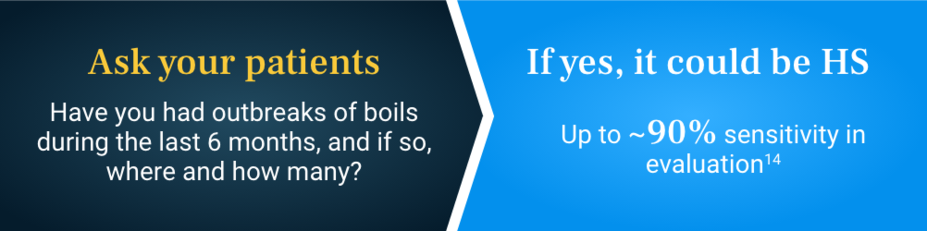
An HS diagnosis requires a physical and historical assessment. There are 3 essential diagnostic criteria for distinguishing HS11
FACT
Many patients first present with symptoms to a primary care physician or non-HS-treating dermatology provider. Recognizing the condition is the first step in getting patients the individualized care they need.2
If you recognize, refer
Management and treatment strategies for HS should be led by an HS-treating dermatology provider.2
Hear from your peers about understanding HS
Healthcare providers with real-world experience managing hidradenitis suppurativa share their knowledge to help provide a deeper disease understanding.
The healthcare providers featured in these videos were compensated for their time. These videos represent their opinions and do not represent the opinions of Novartis.
The facts about HS
HS is widely under-recognized. This can cause diagnostic delays that can facilitate disease progression and long-lasting negative effects on a patient's quality of life.10,15,16 The shame and embarrassment that may be associated with HS can be made worse by misconceptions about its causes, but these can be corrected with education about the condition. Knowing fact from fiction about HS can help get patients the accurate diagnosis and treatment they promptly need.9,10
Hidradenitis suppurativa risk factors and comorbidities
Knowing some of the common risk factors and comorbidities associated with HS can help identify patients early on. Some risk factors may also be comorbidities.31
RISK FACTORS
Female gender10 |
Obesity4,32 |
Family history3,10,18,33 Evaluating family history could help increase the likelihood of a timely diagnosis |
African descent33 |
Active cigarette smoking31 |
Age3,7,10,33 HS flares may be associated with hormonal changes (eg, puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause). It is important to evaluate each patient individually |
BMI, body mass index. |
COMORBIDITIES*
Obesity7 |
Joint spondyloarthropathies31 |
Squamous cell skin cancer31 |
Type 2 diabetes7 |
Polycystic ovary syndrome7 |
Substance-related disorder33,34 |
Metabolic syndrome3,31 |
Depression31,35 |
*Comorbidities are not limited only to those listed. Prevalence is reported as prevalence of comorbidities in patients with HS based on different studies in the medical literature. |
FACT
Given the numerous comorbidities associated with HS, management coordinated between a multidisciplinary care team should be based on the individual.2